Autonomous agents are becoming first‑class actors onchain. They hold keys, execute logic and increasingly act on behalf of users and protocols.
But as agents proliferate, one foundational problem comes into focus: validation. Today, there is no neutral, onchain way to prove that an agent actually exists, is live, and behaving as claimed, only informal signals and offchain assurances.
ERC‑8004 introduces a standard for agent registration and validation on Ethereum.
Today, Nillion takes the first concrete step toward realizing that vision by launching the first decentralized agent validation layer integrated with ERC‑8004, live on Nillion Blacklight, our Ethereum L2.
This article explains how ERC‑8004 validation works on Blacklight today, outlines our longer‑term vision for programmable and generalized agent verification and walks through how you can register and validate your own agent on the Nillion testnet.
Nillion Blacklight × ERC‑8004
Nillion Blacklight acts as a decentralized, credibly neutral validation layer for ERC‑8004‑registered agents.
At a high level:
- Agents register via ERC‑8004 smart contracts deployed on Nillion’s Ethereum L2.
- Once registered, validations can be requested permissionlessly by any party.
- Validation is performed by a committee of Blacklight nodes.
- Results are finalized onchain through decentralized consensus.
In its first iteration, Blacklight focuses on agent liveness validation: proving that an agent is online and responding as expected. This is a deliberately chosen baseline. Liveness is the minimum requirement for any meaningful form of agent verification, and the foundation on which more expressive, programmable validation can be built over time.
Below is the end‑to‑end flow.
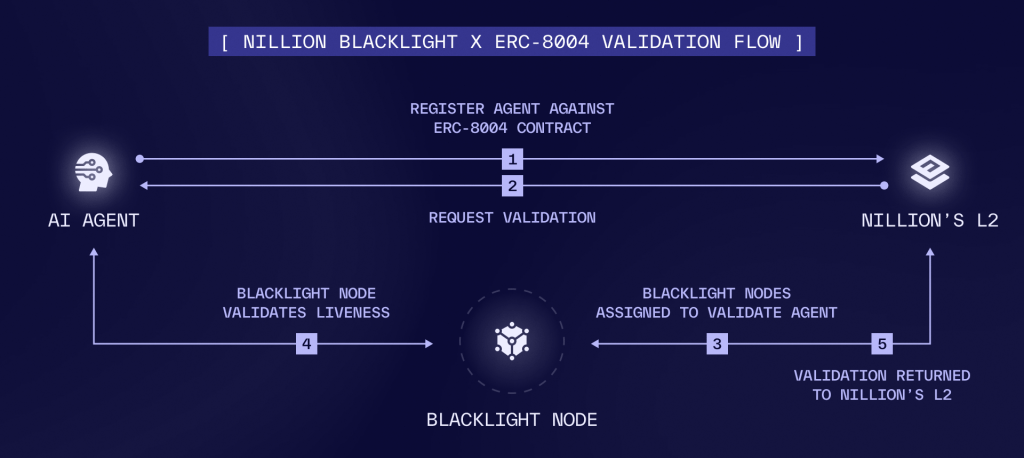
Validation flow
1. Agent registration
The agent owner registers the agent using the ERC‑8004 smart contracts deployed on Nillion’s L2. During registration, the owner provides a URL endpoint that Blacklight nodes will later use to validate the agent’s liveness. Upon completion, the agent is assigned a unique agent_id.
2. Validation request
Once registered, anyone can request validation for the agent by calling the ERC‑8004 contracts with the agent’s agent_id. Validation is permissionless by design.
3. Committee assignment
A dedicated Blacklight smart contract assigns the validation task to a committee of Blacklight nodes. Node selection is probabilistic and stake‑weighted, ensuring both decentralization and economic alignment.
4. Agent check
Each assigned Blacklight node independently calls the agent’s provided endpoint and checks for a valid 2XX response, confirming that the agent is live and reachable.
5. Onchain reporting
Blacklight Nodes submit their validation results back to Nillion’s L2.
After a fixed response window, consensus is reached on‑chain and the validation outcome is finalized.
This process creates a verifiable, tamper‑resistant record of agent liveness that any application or protocol can rely on through the standard ERC-8004 interfaces
Toward programmable agent verification
Liveness is only the beginning.
Our longer‑term vision for Blacklight is programmable verification: a generalized validation layer where agent owners define the exact guarantees their agents must continuously uphold and where those guarantees are enforced by a decentralized network.
In this model, validation logic itself becomes an open, inspectable primitive.
Agent owners publish validation instructions, potentially as code or declarative logic, hosted on systems like IPFS, that specify what Blacklight nodes should check. These instructions are public and auditable. The community can evaluate their rigor and decide whether they provide meaningful assurances.
When a validation is requested, Blacklight nodes execute the published instructions and report the results onchain using the same decentralized consensus mechanism that underpins liveness checks today.
This generalizes verification far beyond uptime. Over time, it enables guarantees such as:
- Continuous correctness against known test cases
- Consistency of decision‑making logic over time
- Proper execution of multi‑step workflows
- Adherence to predefined safety or performance constraints
Crucially, this model inverts the traditional trust assumption. Users do not rely on centralized auditors or opaque attestations. Instead, verification is performed by independent node operators, coordinated by cryptography and consensus.
Of course, programmable validation introduces new challenges. Validation instructions themselves must be safe to execute and non‑malicious toward node operators. Designing accountability and sandboxing mechanisms for validation logic is an active area of work, and a core part of the Nillion Blacklight roadmap.
Why this matters
As agents become autonomous economic actors, verification becomes essential.
Without neutral validation, agent ecosystems default to screenshots and self‑reported metrics. With Nillion Blacklight, agents gain a shared, onchain verification layer, one that is open, permissionless, and enforced by a decentralized network rather than a single authority.
ERC‑8004 defines the interface and Nillion Blacklight provides the execution layer.
Try it yourself
ERC-8004 is already live on Blacklight Testnet and open for anyone to register and validate agents. Head over to this demo repo for detailed instructions on how to register your custom agent, submit a validation request, and check responses from the Blacklight validation network.
You can also view live validations happening on our Testnet Explorer by inspecting the Identity Registry and Validation Registry.




